Woodleigh
| Crater Name | Location | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter (km) | Age (Ma) | Exposed | Drilled | Target Rock** | Bolide Type*** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Woodleigh | Western Australia | S 26° 3' | E 114° 39' | 40 | 364 ± 8 | N | Y | M | - |
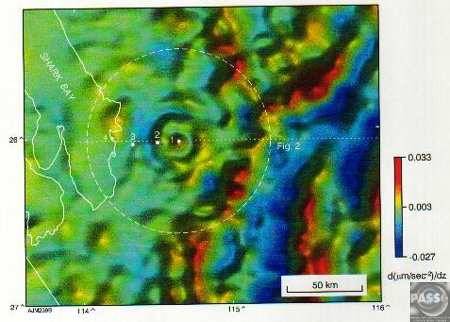
NOTE: The diameter of Woodleigh is contentious - with interpretations ranging from 40 km to 120 km (Mory et al., 2000, Reimold & Koeberl, 2000). Based on the extrapolation of the central peak diameter the rim-crest diameter should be 92-109 km though this is not clearly evident in the geophysical evidence.
1. 1st vertical derivative of the bouguer gravity anomaly Submitted by Andrew Glikson
2. 3D image
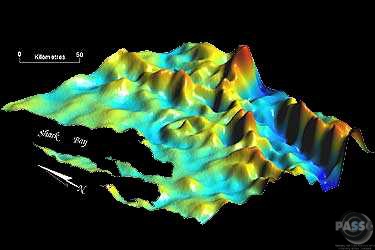
3. DEM image Provided by Dr. Carlos Roberto de Souza Filho
4 & 5. Image Provided by Dr. Carlos Roberto de Souza Filho
References |
Bevan A., Hough R., Hawke P., Morphology and Origin of an Allochthonous Breccia Near the Yallaie Structure, Western Australia - Evidence for Subaqueous Impact, 2004. |
Glikson, A. Y., Eggins, S. , Golding, S. D. , Haines, P. W. , Iasky, R. P. , Mernagh, T. P. , Mory, A. J. , Pirajno, F. and Uysal, I. T., Microchemistry and Microstructures of Hydrothermally Altered Shock-Metamorphosed Basement Gneiss, Woodleigh Impact Structure, Southern Carnarvon Basin, Western Australia. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 52, P. 555 - 573. 2005. |
Glikson, A. Y., Mory, A. J. , Iasky, R. P. , Pirajno, F. , Golding, S. D. and Uysal, I. T., Woodleigh, Southern Carnarvon Basin, Western Australia: history of discovery, Late Devonian Age, and Geophysical and Morphometric Evidence for a 120 km diameter Impact Structure. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 52, P. 545 - 553. 2005. |
Glikson, A.Y., The astronomical connection of terrestrial evolution: Crustal effects of post-3.8 Ga mega-impact clusters and evidence for major 3.2±0.1 Ga bombardment of the Eearth-Moon system, Journal of Geodynamics, v. 32, pp. 205-229, 2001 |
Haines, P. W., Impact Cratering and Distal Ejecta: The Australian Record. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 52, P. 481 - 507. 2005. |
Hough, M., Lee, M.R., Bevan, A,W.R., Shocked quartz and more: Woodleigh impact structure, Western Australia, 64th Annual Meteoritical Society Meeting. 2001. |
Hough, R. M., Lee, M. R. and A. W. R. Bevan., Shocked quartz and more: Woodleigh impact structure, western Australia. Meteoritics and Planetary Science, v 36 Supplement 2001, abstract # 5329. 2001. |
Hough, R.M., Lee, M.R., Bevan, A.W.R., Characterization and significance of shocked quartz from the Woodleigh impact structure, Western Australia, Meteoritics and Planetary Science, v. 38, pp. 1341-1350, 2003 |
Iasky R., Mory A.J., Blundell K.A., The Geophysical Interpretation of the Woodleigh Impact Structure, Southern Carnarvon Basin, Western Australia, 2001. |
Koeberl, C., Hough, R.M., Boamah, D., French, B.M., McDonald,I.and W.U.Riemold., Woodleigh impact structure, Australia: shock petrography and geochemical studies. Meteoritics and Planetary Sciences, v 36, Supplement 2001, abstract # 5281. 2001. |
Macdonald F.A., Mitchell K., New Possible Probable, and Proven Impact Sites in Australia, 2004. |
Macdonald F.A., Bunting J.A., Cina S.E., Yarrabubba - a large, deepy eroded impact structure in the Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia, 2003. |
Mory, A. J., Iasky, R.P., Glikson,A.Y.and F.Pirajno., Response to 'Critical comment on A.J. Mory et al., 2000, Woodleigh, Carnarvon Basin, Western Australia: a new 120 km diameter impact structure' by W.U. Reimold and C. Koeberl. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, v 184, p 359-365. 2000. |
Mory, A.J., et al., Woodleigh, Carnarvon Basin, Western Australia: A new 120 km diameter impact structure, Earth and Planetary Science Letters, v. 177, pp. 119-128, 2000 |
Pirajno, F., Hydrothermal processes associated with meteorite impact structures: Evidence from three Australian examples and implications for economic resources, Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, v. 52, pp. 587-605, 2005 |
Reimold, W. U., Koeberl, C., Critical Comment on: A.J. Mory et al. 'Woodleigh, Carnavon Basin, Western Australia: A New 120 km diameter Impact Structure, EPSL v. 184, pp. 353-7. 2000. |
Reimold, W. U., Koeberl, C., Hough, R.M., McDonald, I., Bevan, A., Amare, K., French,B.M., Woodleigh impact structure, Australia: Shock petrography and geochemical studies, Meteoritics & Planetary Science 38, Nr 8, 1109 - 1130. 2003. |
Renne, P. R., Reimold, W. U. , Koeberl, C. , Hough, R. and Claeys, P., Coment on : "K-Ar evidence from illitic clays of a Late Devonian age for the 120 km diameter Woodleigh impact structure, Southern Carnarvon Basin, Western Australia", by I.T. Uysal, S.D. Golding, A.Y. Glikson, A.J. Mory and M. Glikson. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 201, P. 247 - 252. 2002. |
Renne, P. R., Reimold, W.U., Koeberl, C., Hough, R., Claeys,P., Comment on: "K-Ar evidence from illitic clays of a Late Devonian age for the 120 km diameter Woodleigh impact structure, Southern Carnarvon Basin, Western Australia", by I.T. Uysal, S.D. Golding, A.Y. Glikson, A.J.Mory and M.Glikson, A.Y. Glikson, A.J…. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, v.201, p.247-252. 2002. |
Tonguç Uysal, I., et al., Clay mineralogical, geochemical and isotopic tracing of the evolution of the Woodleigh impact structure, Southern Carnarvon Basin, Western Australia, Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, v. 149, pp. 576-590, 2005 |
Uysal, I. T., Golding, S.D., Glikson, A.Y., Mory, A.J., Glikson, M., Iasky, R.P., Pirajno,F., Discussion: Reply to "Comment on: 'K-Ar evidence from illitic clays of a Late Devonian age for the120 diameter Woodleigh impact structure, Soutern Carnarvon Basin, Western Australia", Earth and Planetary Science Letters, v.201, p.253-260. 2002. |
Uysal, I. T., Golding, S.D., Glikson, A.Y., Mory,A.J.and M.Glikson., K-Ar evidence from illitic clays of a Late Devonian age for the 120 km diameter Woodleigh impact structure, Souther Carnarvon Basin, Western Australia, Earth and Planetary Science Letters, v 192, p 281-289. 2001. |
Uysal, I. T., Mory, A. J. , Golding, S. D. , Bolhar, R. and Collerson, K. D., Clay mineralogical, geochemical and istopic tracing of the evolution of the Woodleigh impact structure, Southern Carnarvon Basin, Western Australia. Contrib Mineral Petrol, Vol. 149, P. 576 - 590. 2005. |
Uysal, T., Golding, S., Glikson, A.Y. and Mory,A.J., K-Ar and oxygen isotopic constraints of illitic clays on the timing and evolution of the Woodleigh impact structure, Carnarvon Basin, Western Australia, Earth Planetary Letters, Vol 192(3), 281-289. 2001. |
| * pre-1977 K-Ar, Ar-Ar and Rb-Sr ages recalculated using the decay constants of Steiger and Jager (1977) Ages in millions of years (Ma) before present. ** Abbreviations: C - Crystalline Target; C-Ms - Metasedimentary Target; M - Mixed Target (i.e.sedimentary strata overlying crystalline basement); S - sedimentary target (i.e. no crystalline rocks affected by the impact event). From Osinski. G. R., Spray J. G., and Grieve R. A. F. 2007. Impact melting in sedimentary target rocks: A synthesis. In The Sedimentary Record of Meteorite Impacts, Geological Society of America Special Paper. Editors: Evans K. Horton W., King D., Morrow J., and Warme J. Geological Society of America: Boulder, in press. ***From Koeberl,C. Identification of meteoritic components in impactites. 1998, Koeberl, C. The Geochemistry and Cosmochemistry of Impacts. 2007 and PASSC Files. (IAB, IIIAB, IIIB, IIID - Iron Meteorite) |

 Woodleigh MDE.jpg)
 Woodleigh Landsat Figura 2D RGB 432.jpg)
 Woodleigh Figuras 3D RGB (Ex 100).jpg)