Wabar
| Crater Name | Location | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter (km) | Age (Ma) | Exposed | Drilled | Target Rock** | Bolide Type*** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wabar | Saudi Arabia | N 21° 30' | E 50° 28' | 0.11 | 0.00014 | Y | Y | S | IIIAB iron |
1. Photograph by Jeff Wynn
2. Photo of the remaining rim of the largest crater. The crater was 12.5 meters deep in 1932, 8 meters deep in 1965, and a bit over 2 meters deep in 1994 (this photo). Courtesy Jeff Wynn
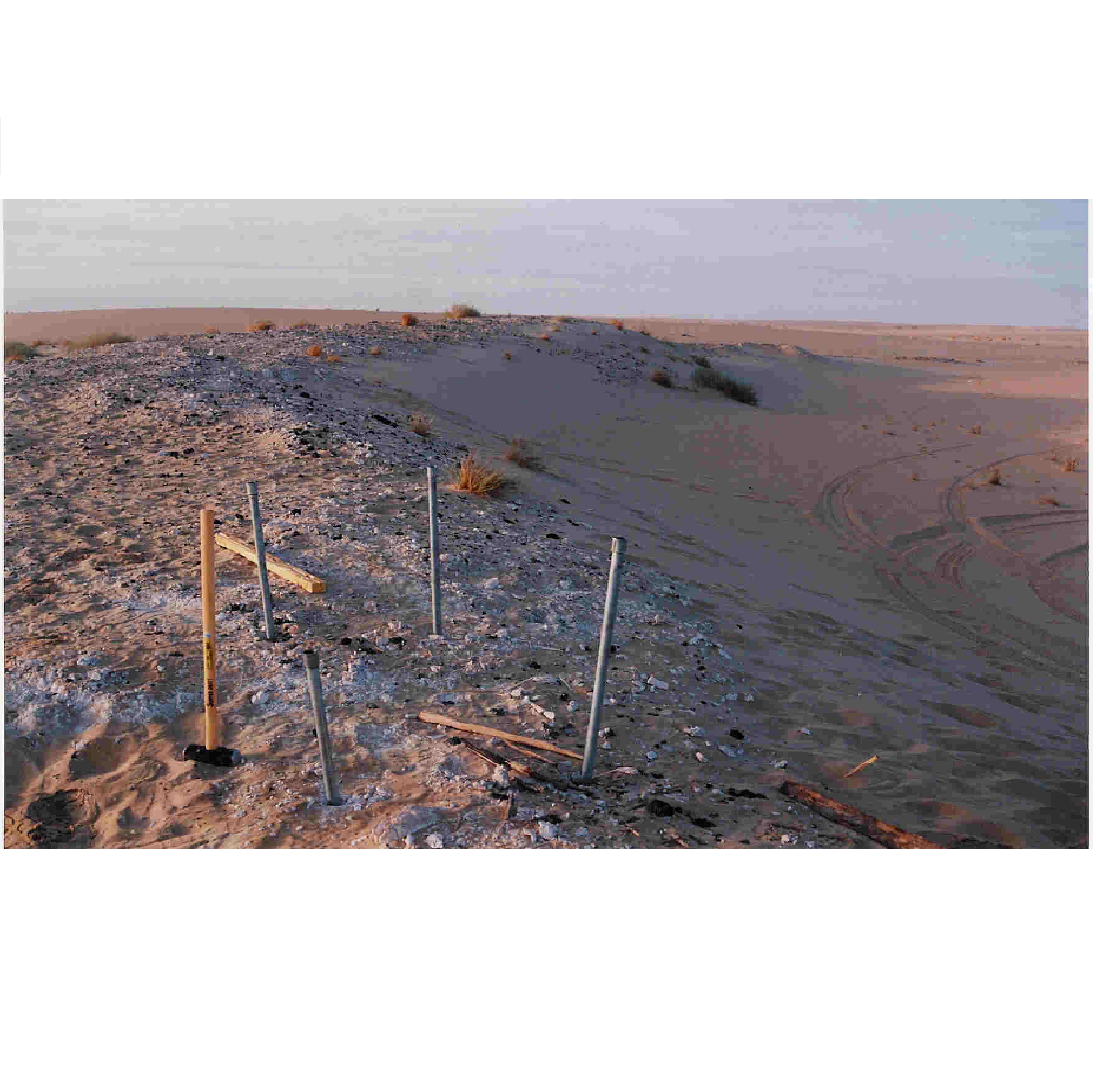
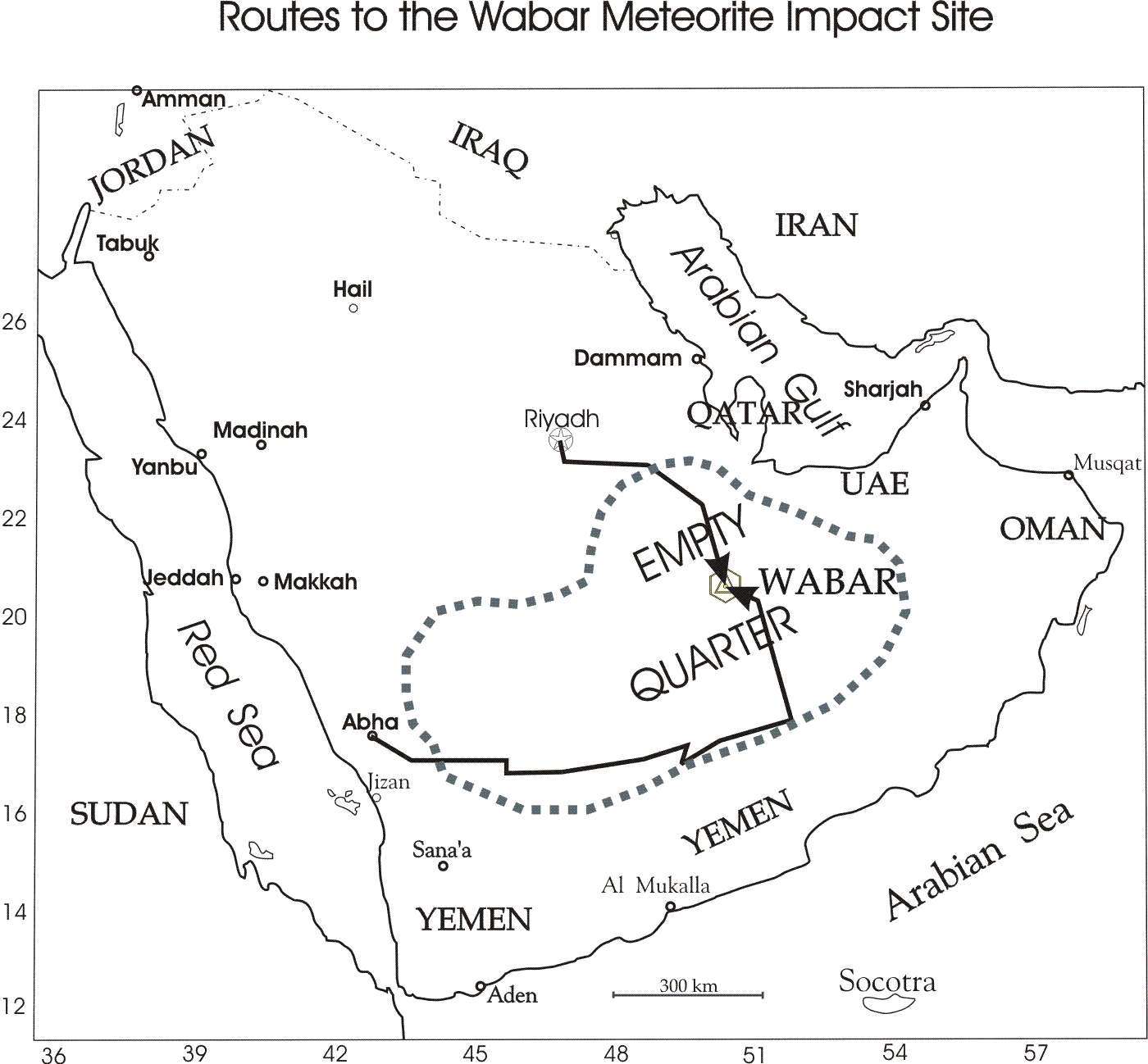
3. Expedition tracks made during the three expeditions undertaken to map the Wabar meteorite impact site Courtesy Jeff Wynn
4. Photo shows what happened to ~99.99% of the incoming bolide: It was uniformly mixed to generate the ubiquitous "Wabar Glass", which is uniformly 90% local sand and 10% nickle-iron asteroid. Courtesy Jeff Wynn
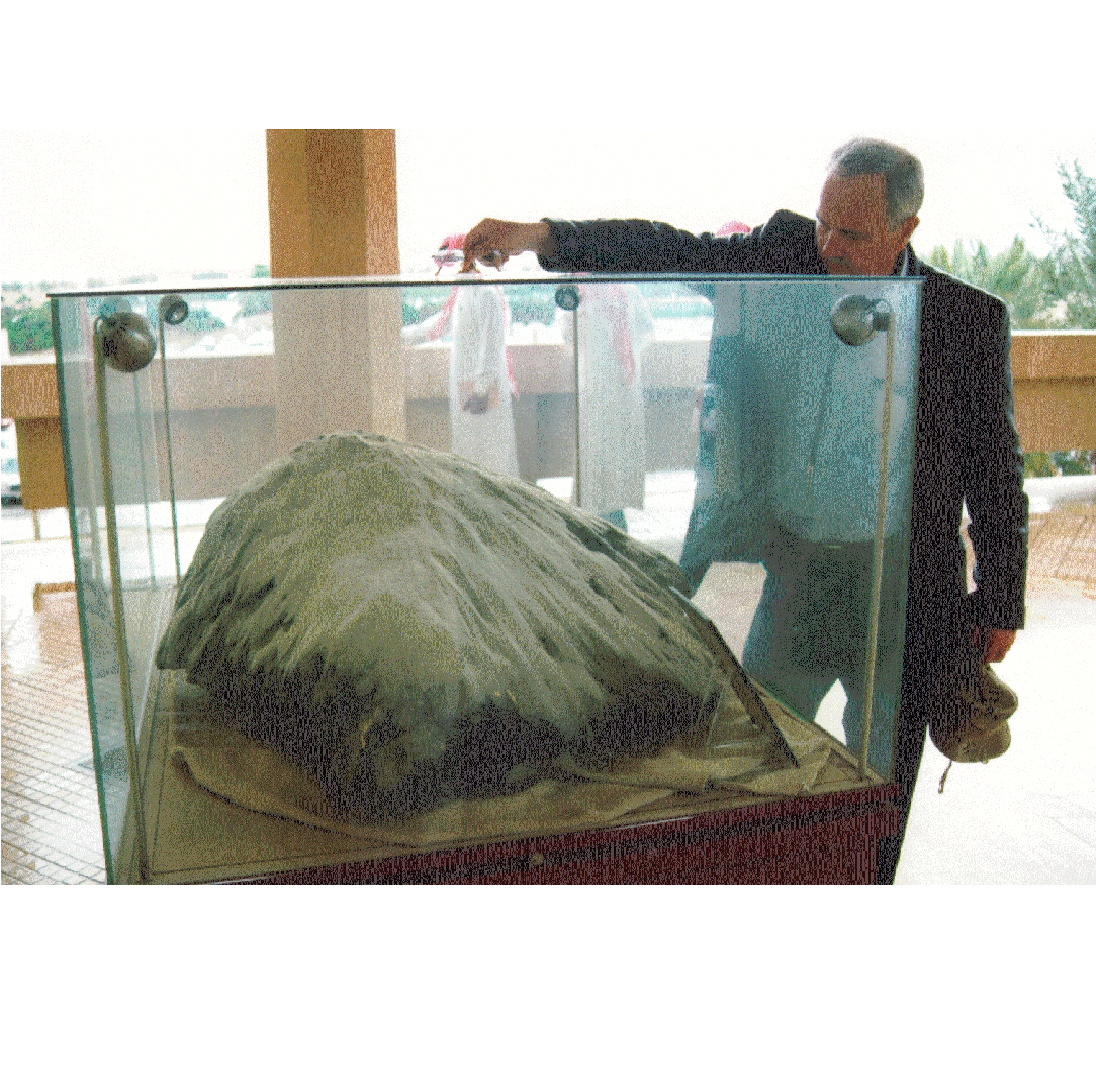
5. This is a photo of the largest surviving fragment of the Wabar bolide (Gene Shoemaker in the background), recovered in 1965. Courtesy Jeff Wynn
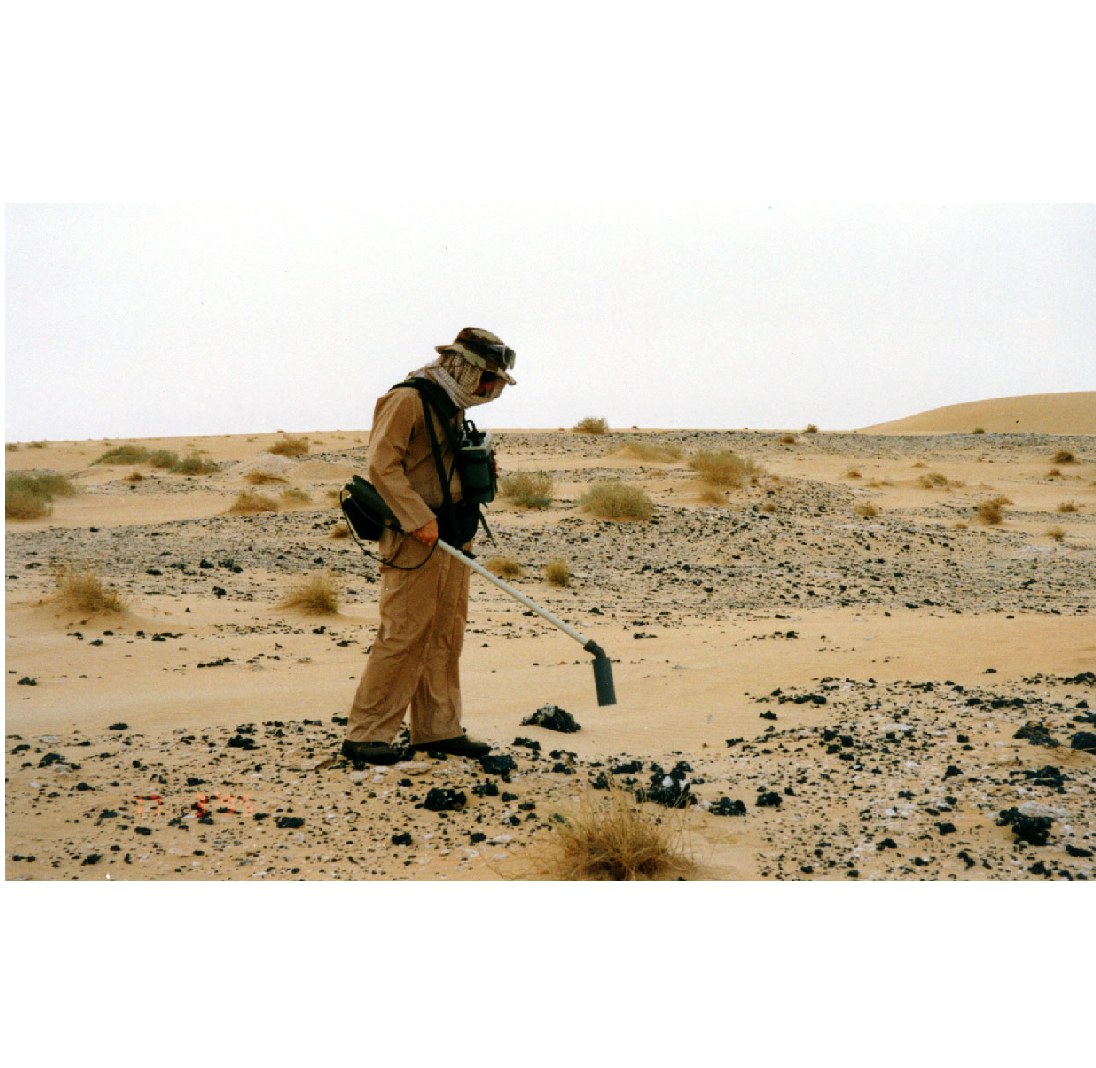
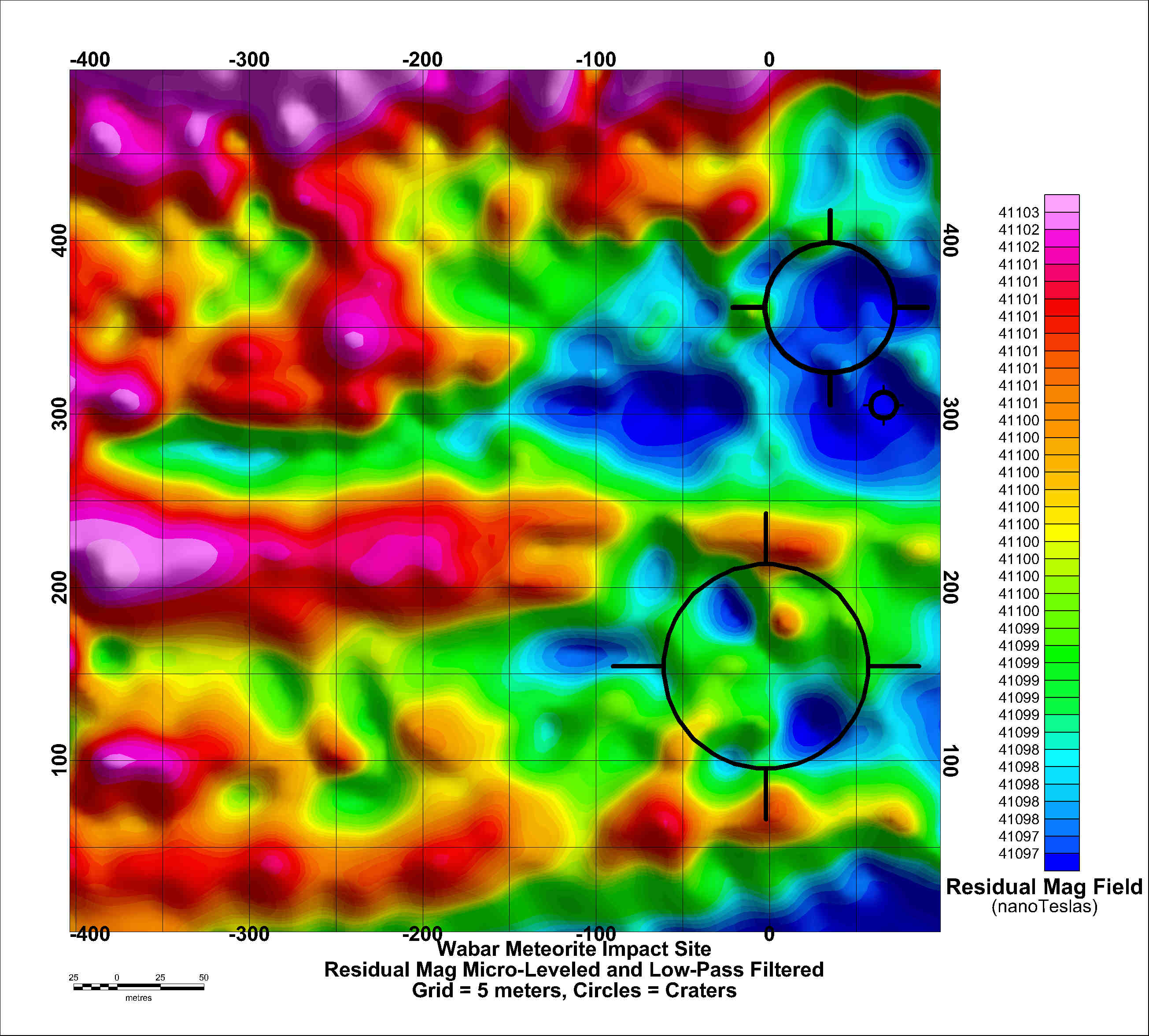
6. Photograph of Jeff Wynn conducting a high-resolution magnetic survey with a cesium-vapor magnetometer. Courtesy Jeff Wynn
7. Results of a magnetic survey conducted over 5 days at the Wabar meteorite impact site. Courtesy Jeff Wynn
References |
Almohandis, A. A., The Wabar meteorite and its impact crater, Saudi Arabia (abstract). GAC/MAC, Program with Abstracts, Annual Meeting, v. 19, p. A2. 1994. |
Bartrum, C. M., Meteorite craters in Arabia and Ashanti. British Astronomical Association Journal, v. 42, pp. 398-399. 1932. |
Basilevsky, A. T., Fel'dman, V.I., Kapustkina, I.G. and Kolesov,G.M., On the distribution of iridium in the rocks of terrestrial impact craters (in Russian). Geokhimiya, v. 6, pp. 781-790. 1984. |
Brett, R., Metallic spherules in impactite and tektite glasses (abstract). French, B.M. and Short, N.M., eds., Shock Metamorphism of Natural Materials, Mono Book Corp., Baltimore, MD, p. 623. 1968. |
Brett, R., Metallic spherules in impactite and tektite glasses. American Mineralogist, v. 52, pp. 721-733. 1967. |
Bunch, T. E., Cohen, A. J., Shock deformation of quartz from two meteorite craters. Geological Society of America, Bulletin, v. 75, pp. 1263-1266. 1964. |
Chao, E. C. T., Fahey, J.J. and Littler,J., Coesite from Wabar crater, near Al Hadida, Arabia. Science, v. 133, pp. 882-883. 1961. |
Chao, E. C. T., Shock effects in certain rock-forming minerals. Science, v. 156, pp. 192-202. 1967. |
Gibbons, R. V., Horz, F. and Morris,R.V., Fractionation of metallic spherules in Wabar, Henbury, and Monturaqui impactites (abstract). EOS, v. 56, pp. 1017. 1975. |
Gibbons, R. V., Horz, F., Thompson, T.D. and Brownlee,D.E., Metal spherules in Wabar, Monturaqui, and Henbury impactites. Proceedings Lunar and Planatary Science Conference 7th, pp. 863-880. 1976. |
Grieve, R. A. F., The record of impact on Earth: Implications for a major Cretaceous/Tertiary impact event. Geological Society of America, Special Paper 190, pp. 25-37. 1982. |
Gurov, E. P., Gurova, E. P., Impact structures on the Earth's surface (in Russian). Geologicheskii Zhurnal, v. 47, pp. 117-124. 1987. |
Gurov, E. P., Gurova, E. P., Impact-melt composition of the Oblon crater: Chlorine as a possible indicator of the submarine crater formation (abstract). Meteoritics, v. 30, pp. 515. 1995. |
Holm, D. A., New meteorite localities in the Rub al Khali, saudi Arabia. American Journal of Science, v. 260, pp. 303-309. 1962. |
Hörz, F., Mittlefehldt, D W. and See,T H., Dissemination and fractionation of projectile material in impact melts from the Wabar crater, Saudi Arabia (abstract). Meteoritics, v. 26, pp. 346-347. 1991. |
Hörz, F., See, T H., Murali, A V. and Blanchard,D P., Heterogeneous dissemination of projectile materials in the impact melts from Wabar crater, Saudi Arabia. Proceedings Lunar and Planetary Science Conference 19th, pp. 697-709. 1989. |
Johnson, P. H., Bogard, D.D. and Horz,F., Shock-implanted noble gases in samples from the Wabar impact crater: Implications for other terrestrial craters and the surface of Mars (abstract). Lunar and Planetary Science XIX, pp. 557-558. 1988. |
Kaputskina, I. G., Fel'dman, V. I., Fractionation of meteoritic material in the impact process (in Russian). Geokhimiya, v. 11, pp. 1547-1557. 1988. |
Krinov, E. L., Meteorite craters on the Earth's surface. Middlehurst, B.M. and Kuiper, G.P., eds., The Moon, Meteorites and Comets, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, v. IV, pp. 183-207. 1963. |
Marvin, U. B., The impact of Wabar (abstract). International Geological Congress, 25th, Sydney, Australia, v. 3, p. 925. 1976. |
Masaitis, V. L., Danilin, A.N., Maschak, M.S., Raykhlin, A.I., Selivanovskaya, T.V. and Shadenkov,Ye.M., The Geology of Astroblemes (in Russian). Leningrad, Nedra, 231 p. 1980. |
McCall, G. J. H., The Wabar craters. McCall, G.J.H., ed., Meteorite craters, Dowden, Hutchinson and Ross, Inc., Stroudsburg, Pa., pp. 97-98. 1977. |
McHone J F., Dietz, R. S., Earth's multiple impact craters and astroblemes (abstract). Lunar and Planetary Science, v. XXIII, pp. 887-888. 1992. |
McHone, J. F., Dietz, R. S., Earth's multiple impact craters and astroblemes (abstract). Lunar and Planetray Science XXIII, pp. 887-888. 1992. |
Mittlefehldt, D. W., See, T.H. and Horz,F., Dissemination and fractionation of projectile materials in the impact melts from Wabar Crater, Saudi Arabia. Meteoritics, v. 27, pp. 361-370. 1992. |
Murali, A. V., See, T.H. and Blanchard,D.P., Precursor of the Wabar crater glasses? (abstract). Lunar and Planetary Science XIX, pp. 815-816. 1988. |
Newsom, H.E. and Boslough, M.B.E., Impact melt formation by low-altitude airburst processes, evidence from small terrestrial craters and numerical modeling, Lunar and Planetary Science Conference XXXIX, abstract #1460. 2008. |
Philby, H.StJ.B, The Empty Quarter: Henry Holt and Co., New York, 432 p. 1933. |
Prescott, J., Robertson, G., Shoemaker, C., Shoemaker, E.C. and Wynn, J.C., Luminescence dating of the Wabar meteorites craters, Saudia Arabia. Journal of Geophysical Research, v. 109, E01008, doi: 10.1029/2003JE002136. 2004. |
Rocca, M. C. L., A Wabar like site in eastern Uruguay? Meteoritics & Planetary Science, v.36, n.9, p.A176. 2001. |
Sclar, C. B., Short, N.M. and Cocks,G.G., Shock-wave damage in quartz as revealed by electron and incident-light microscopy. French, B.M. and Short, N.M., eds., Shock Metamorphism of Natural Materials, Mono Book Corp., Baltimore, MD, pp. 483-494. 1968. |
See, T. H., Horz, F. and Murali,A.V., Two types of impact melt from the Wabar crater, Saudi Arabia (abstract). Lunar and Planetary Science XIX, pp. 1053-1054. 1988. |
See, T. H., Mittlefehldt, D.W. and Horz,F., Analysis of aeroballistically dispersed glass samples from Wabar crater, Saudi Arabia (abstract). Lunar and Planetary Science XX, pp. 980-981. 1989. |
See, T. H., Mittlefehldt, D.W., Horz. F. and Wasson,J.T., Projectile dissemination and fractionation at Wabar crater, Saudi Arabia (abstract). Lunar and Planetary Science XXI, pp. 1123-1124. 1990. |
Shoemaker, E. M., Wynn, J. C., Geology of the Wabar meteorite craters, Saudi Arabia (abstract). Lunar and Planetary Science XXVIII, pp. 1313-1314. 1997. |
Short, N. M., Shock-lithification of unconsolidated rock materials. Science, v. 154, pp. 382-384. 1966. |
Spencer, L. J., Hey, M. H., Meteoric iron and silica-glass from the meteorite craters of Henbury (central Australia) and Wabar (Arabia). Mineralogical Magazine, v. 23, pp. 387-404. 1933. |
Storzer, D., Fission track dating of some impact craters in the age range between 6,000y and 300 m.y. (abstract). Meteoritics, v. 6, p. 319-320. 1971. |
Val'ter, A. A., Gurov, E. P., The system of mineralogical indicators in factors of shock metamorphism in granitoid rocks (in Russian). Kosmicheskaya mineralogiya, v. 11, pp. 92-102. 1978. |
Wynn J.C., Shoemaker, E. M., Secrets of the Wabar craters. Sky & Telescope, pp. 44-48. 1997. |
Wynn, J. C., Mapping an Iron-Meteorite Impact Site with a Magnetometer, and Implications for the Probablility of a Catastrophic Impact on Earth. Journal of Environmental & Engineering Geophysics, Vol. 7, Issue 4, P. 143 - 150. 2002. |
Wynn, J. C., The day the sands caught fire, Scientific American Magazine P. 64 - 71. 1998. |
Xue, S., Herzog, G.F. and Hall,G.S., Stable nickel isotopes in fusion crusts from iron meteorites and from metallic particles in a black Wabar impact glass (abstract). Meteoritics, v. 28, pp. 462. 1993. |
Zotkin, I. T., "Moon" craters on the Earth (in Russian). Priroda, v. 9, pp. 95-105. 1969. |
Zotkin, I. T., Tsvetkov, V. I., Searches for meteorite craters on the Earth (in Russian). Astronomicheskii Vestnik, v. 4, pp. 55-56. 1970. |
| * pre-1977 K-Ar, Ar-Ar and Rb-Sr ages recalculated using the decay constants of Steiger and Jager (1977) Ages in millions of years (Ma) before present. ** Abbreviations: C - Crystalline Target; C-Ms - Metasedimentary Target; M - Mixed Target (i.e.sedimentary strata overlying crystalline basement); S - sedimentary target (i.e. no crystalline rocks affected by the impact event). From Osinski. G. R., Spray J. G., and Grieve R. A. F. 2007. Impact melting in sedimentary target rocks: A synthesis. In The Sedimentary Record of Meteorite Impacts, Geological Society of America Special Paper. Editors: Evans K. Horton W., King D., Morrow J., and Warme J. Geological Society of America: Boulder, in press. ***From Koeberl,C. Identification of meteoritic components in impactites. 1998, Koeberl, C. The Geochemistry and Cosmochemistry of Impacts. 2007 and PASSC Files. (IAB, IIIAB, IIIB, IIID - Iron Meteorite) |