Chesapeake Bay
| Crater Name | Location | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter (km) | Age (Ma) | Exposed | Drilled | Target Rock** | Bolide Type*** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chesapeake Bay | Virginia, U.S.A. | N 37° 17' | W 76° 1' | 40 | 35.5 ± 0.3 | N | Y | M | - |
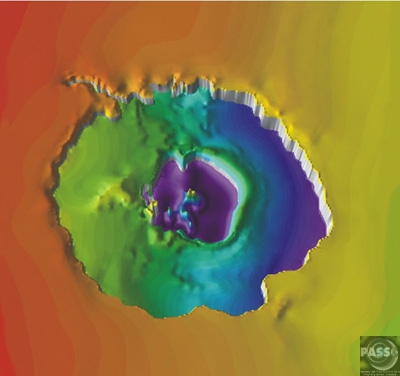
1. 3D model of the crater looking obliquely to the north. Supplied by C. Wylie Poag
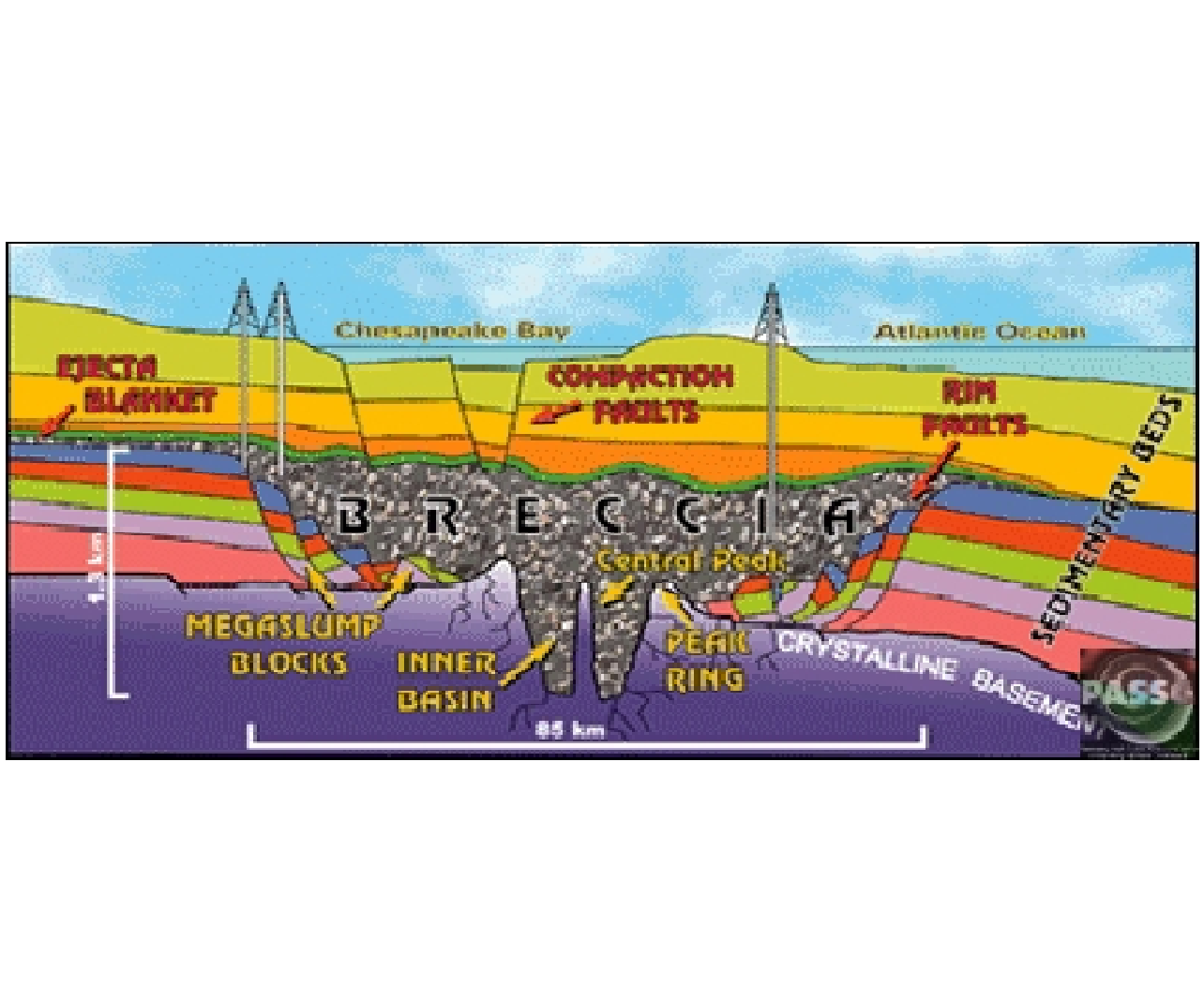
2. Cross Section Diagram by C. Wylie Poag USGS
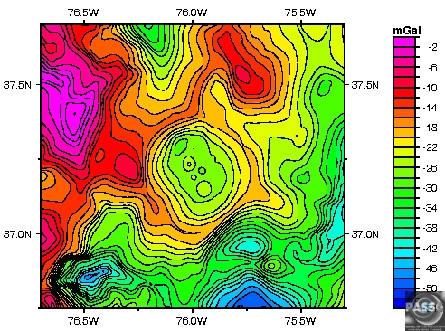
3. Gravity Map
References |
| Albin, E. F., Norman, M.D. and Roden,M.F., Geochemistry of Georgia tektites: Evidence for a compositionally diverse source (abstract). Meteoritics & Planetary Science, v. 31, pp. A5-A6. 1996. |
| Bartosova, K., et al., Geochemistry of the impact breccia section (1397-1551 m depth) of the Eyreville drill core, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, USA, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 397-433, 2009 |
| Bartosova, K., et al., Melt in the impact breccias from the Eyreville drill cores, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, USA, Meteoritics and Planetary Science, v. 46, pp. 396-430, 2011 |
| Bartosova, K., et al., Petrographic and shock metamorphic studies of the impact breccia section (1397-1551 m depth) of the Eyreville drill core, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, USA, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 317-348, 2009 |
| Bartosova, K., et al., Petrography, mineralogy, and geochemistry of deep gravelly sands in the Eyreville B core, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Meteoritics and Planetary Science, v. 45, pp. 1021-1052, 2010 |
| Bartosova, K., Koeberl, C., Shock-metamorphism investigations of quartz grains in clasts from impact breccia of the Eyreville B drill core, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, USA, Meteoritics and Planetary Science, N/A, Article in Press (2011) |
| Belkin, H.E., Horton Jr., J.W., Silicate glasses and sulfide melts in the ICDP-USGS Eyreville B core, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Virginia, USA, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 447-468, 2009 |
| Bleibinhaus, F., Lester, R.W., Hole, J.A., Applying waveform inversion to wide-angle seismic surveys, Tectonophysics, v. 472, pp. 238-248, 2009 |
| Browning, J.V., et al., Integrated sequence stratigraphy of the postimpact sediments from the Eyreville core holes, Chesapeake Bay impact structure inner basin, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 775-810, 2009 |
| Catchings, R. D., Powars, D.S., Gohn, G.S., Goldman, M.R., Gandhok,G.and G.H.Johnson., Subsurface images of the annular trough of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Virginia from seismic reflection/refraction data. Lunar and Planetary Science XXXII. 2001. |
| Catchings, R.D., et al., Anatomy of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure revealed by seismic imaging, Delmarva Peninsula, Virginia, USA, Journal of Geophysical Research B: Solid Earth, v. 113, article number B08413, 2008 |
| Catchings, R.D., et al., High-resolution seismic-reflection image of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia, US Geological Survey Professional Paper, Issue 1688, pp. I1-I21, 2006 |
| Coccioni, R., Frontalini, F., Spezzaferri, S., Late Eocene impact-induced climate and hydrological changes: Evidence from the Massignano global stratotype section and point (central Italy), Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 452, pp. 97-118, 2009 |
| Cockell, C.S., et al., Microbial abundance in the deep subsurface of the Chesapeake Bay impact crater: Relationship to lithology and impact processes, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 941-950, 2009 |
| Collins, G. S., Melosh, H. J., Hydrocode Simulations of the Chesapeake Bay Impact, Lunar and Planetary Science XXXV. 2004. |
| Collins, G.S., Wunnemann, K., How big was the Chesapeake Bay impact? Insight from numerical modeling, Geology, v. 33, pp. 925-928, 2005 |
| Declercq, J., et al., Experimental alteration of artificial and natural impact melt rock from the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 559-569, 2009 |
| Deutsch, A., Koeberl, C., Establishing the link between the Chesapeake Bay impact structure and the North American tektite strewn field : The Sr-Nd isotopic evidence, Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 41, Nr 5, P. 689 - 703. 2006. |
| Durand, C.T., et al., Supplemental materials for the ICDP-USGS Eyreville A, B, and C core holes, Chesapeake Bay impact structure: Core-box photographs, coring-run tables, and depth-conversion files, Special Paper of the Geological Association of America, Issue 458, pp. 115-118, 2009 |
| Dypvik, H., Jansa, L. F., Sedimentary signatures and processes during marine bolide impacts: a review, Sedimentary Geology v. 161, p. 309-337. 2003. |
| Edwards, L. E., Powars, D. S., Impact damage to dinocysts from the late Eocene Chesapeake Bay event, Palaios 18, 275-285. 2003. |
| Edwards, L.E., et al., Geologic columns for the ICDP-USGS Eyreville A and C cores, Chesapeake Bay impact structure: Postimpact sediments, 444 to 0 m depth, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 91-114, 2009 |
| Ferrell Jr., R.E., Dypvik, H., The mineralogy of the Exmore beds- Chickahominy Formation boundary section of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure revealed in the Eyreville core, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 723-746, 2009 |
| Ferriere, L., et al. , Ballen quartz and cristobalite in impactites: New investigations, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 465, pp. 609-918, 2010 |
| Gibson, R. L., Townsend, G. N., Horton, J. W., Kunk, M. J., & Zack, T., Age of mid-amphibolite facies alleghanian metamorphism in rocks from the icdp-usgs eyreville-b core, chesapeake bay impact structure, virginia. Paper presented at the , 43(5) 437-437. 2011. |
| Gibson, R.L., et al., Pre-impact tectonothermal evolution of the crystalline basement-derived rocks in the ICDP-USGS Eyreville B core, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 235-254, 2009 |
| Glass B.P., McHugh C.M.G., More Upper Eocene (Norht American) Tekties and Impact Ejecta off New Jersy, 1996. |
| Goderis, S., et al., Siderophile elements from the Eyreville drill cores of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure do not constrain the nature of the projectile, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 465, pp. 395-409, 2010 |
| Gohn, G. S., Bruce, T.s., Catchings, R.D., Emry, S.R., Johnson, G.H., Levine, J.S., McFarland, E.R., Poag,C.W.and D.S.Powars., Integrated geologic, hydrologic and geophysical investigations of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Virginia, USA: a multi-agency program, Lunar and Planetary Science XXXII. 2001. |
| Gohn, G. S., Koeberl, C. , Miller, K. G. , Reimold, W. U. , Cockell, C. , Horton Jr., J. W. , Sanford, W. E. and Voytek, M. A., Chesapeake Bay Impact Structure Drilled, EOS, Vol 87, No. 35, P. 349 - 360. 2006. |
| Gohn, G. S., Powars, D., Bruce, T.S., Self-Trail, J.M., Weems, R.E., Edwards, L.E., Horton, J.W.Jr., Izett, G.A. and Johnson,G.H., Preliminary interpretation of the USGS-NASA Langley Corehole, Chesapeake Bay Impact Structure, York-James Peninsula, Hampton, VA, Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, v. 33, no. 2, p. A-24. Southeastern Section - 50th Annual Meeting (April 5-6, 2001). 2001. |
| Gohn, G.S., et al., Deep drilling in the Chesapeake Bay impact structure - An overview, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 1-20, 2009 |
| Gohn, G.S., et al., Deep drilling into the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Science, v. 320, pp. 1740-1745, 2008 |
| Gohn, G.S., et al., Physical geology of the impact-modified and impact-generated sediments in the USGS-NASA Langley core, Hampton, Virginia, US Geological Survey Professional Paper, Issue 1688, pp. C1-C38, 2006 |
| Gohn, G.S., et al., Rock-avalanche and ocean-resurge deposits in the late Eocene Chesapeake Bay impact structure: Evidence from the ICDP-USGS Eyreville cores, Virginia, USA, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 587-615, 2009 |
| Harris R.S., Roden M.F., Schroeder P.A., Holland S.M., Duncan M.S.,Albin E.F., Upper Eocene impact horizon in east-central Georgia, Geology, v.32, p.717-720. 2004. |
| Harvey, S. V., Investigating the relationship of the Chesapeake Bay impact crater and the Virginia inland salt-water wedge, Bolide Impacts on Wet Targets, Geological Society of America Field Forum Abstracts. 2001. |
| Hayden, T., et al., Impact effects and regional tectonic insights: Backstripping the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Geology, v. 36, pp. 327-330, 2008 |
| Heidinger, P., et al., First results of geothermal investigations, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Eyreville core holes, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 931-940, 2009 |
| Horton Jr., J.W., et al., Chesapeake Bay impact structure: Morphology, crater fill, and relevance for impact structures on Mars, Meteoritics and Planetary Science, v. 41, pp. 1613-1624, 2006 |
| Horton Jr., J.W., et al., Evolution of crystalline target rocks and impactites in the chesapeake bay impact structure, ICDP-USGS eyreville B core, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 277-316, 2009 |
| Horton Jr., J.W., et al., Origin and emplacement of impactites in the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Virginia, USA, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 437, pp. 73-97, 2007 |
| Horton Jr., J.W., et al., Petrography, structure, age, and thermal history of granitic coastal plain basement in the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, USGS-NASA Langley core, Hampton, Virginia, US Geological Survey Professional Paper, Issue 1688, pp. B1-B28, 2006 |
| Horton Jr., J.W., et al., Recent research on the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, USA - Impact debris and reworked ejecta, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 384, pp. 147-170, 2005 |
| Horton Jr., J.W., Powars, D.S., Gohn, G.S., Studies of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure - Introduction and discussion, US Geological Survey Professional Paper, Issue 1688, pp. A2-A23, 2006 |
| Horton, J.W., Jr., and Izett, G.A., Crystalline-rock ejecta and shocked minerals of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, USGS-NASA Langley Core, Hampton, Virginia, with supplemental constraints on the age of the impact, in Horton et al., Editors, Studies of the Chesapeake Bay Impact Structure—The USGS-NASA Langley Corehole, Hampton, Virginia, and related Coreholes and Geophysical Surveys, USGS Prof. Paper 1688. |
| Jackson, J.C., et al., A shock-induced polymorph of anatase and rutile from the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Virginia, U.S.A, American Mineralogist, v. 91, pp. 604-608, 2006 |
| Jackson, J.C., et al., Monoclinic tridymite in clast-rich impact melt rock from the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, American Mineralogist, v. 96, pp. 81-88, 2011 |
| Johnson, G. H., Kruse, S.E., Vaughn, A.W., Lucey, J.K., Hobbs, C.H. III, Powars,D.S., Postimpact Deformation Associated with the Late Eocene Chesapeake Bay Impact Structure in Southeastern Virginia, Geology; June 1998, v. 26; no. 6; p.507-510. 1998. |
| Kerr, R. A., Making an impact under the Chesapeake. Science, v. 265, pp. 1036. 1994. |
| Koeberl, C., Anderson, R. R., Manson and Company: Impact structures in the United States. Geological Society of America Special PaperXXX (in press). 1995. |
| Koeberl, C., Continental scientific drilling and the study of terrestrial impact craters, First International Conference on Impact Cratering in the Solar System. 2006. |
| Koeberl, C., Kruger, F. J. and C. W. Poag., Geochemistry of surficial sediments near the Chesapeake Bay impact structure and the search for source rocks of the North American tektites, Lunar and Planetary Science XXXII. 2001. |
| Koeberl, C., Late Eocene impact craters and impactoclastic layers-An overview, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 452, pp. 17-26, 2009 |
| Koeberl, C., Milkereit, B., Continental Drilling and the Study of Impact Craters and Processes - an ICDP Perspective, In: Continental Scientific Drilling (eds. Harms, U., Koeberl, C., and Zoback, M.D.), Springer, Heidelberg, p. 95-161. 2007. |
| Koeberl, C., Poag, C.W., Reimold, W.U. and Brandt,D., Impact origin of Chesapeake Bay structure and the source for the North American tektites. Science, v. 271, pp. 1263-1266. 1996. |
| Koeberl, C., Reimold, W.R., Brandt, D. and Poag,C.W., Stalking the Late Eocene impact: Geochemistry of rocks from the Chesapeake Bay crater and North American tektites (abstract). 4th International Workshop of the ESF Scientific Network on "Impact Cratering and Evolution of Planet Earth". The Role of Impacts on the Evolution of the Atmosphere and Biosphere with Regard to Short- and Long-Term Changes, pp. 102-103. 1995. |
| Koeberl, C., Reimold, W.U., Brandt, D. and Poag,C.W., Chesapeake Bay crater, Virginia: Confirmation of impact origin (abstract). Meteoritics, v. 30, pp. 528-529. 1995. |
| Kulpecz, A.A., et al., Postimpact deposition in the Chesapeake Bay impact structure: Variations in eustasy, compaction, sediment supply, and passive-aggressive tectonism, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 811-837, 2009 |
| Kunk, M. J., Horton, J. W., Gibson, R. L., Zack, T., McAleer, R. J., & Townsend, G. N., Alleghanian thermal history of basement-derived target rocks in the icdp-usgs eyreville-b core from the chesapeake bay impact structure. Paper presented at the , 43(5) 550-550. 2011. |
| Larsen, D., Stephens, E.C., Zivkovic, V.B., Postimpact alteration of sedimentary breccias in the ICDP-USGS Eyreville A and B cores with comparison to the Cape Charles core, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Virginia, USA, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 699-721, 2009 |
| Lee, S.R., Horton Jr., J.W., Walker, R.J., Confirmation of a meteoritic component in impact-melt rocks of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Virginia, USA - Evidence from osmium isotopic and PGE systematics, Meteoritics and Planetary Science, v. 41, pp. 819-833, 2006 |
| Malinconico, M.L., Sanford, W.E., Wright Horton Jr., W.J.J., Postimpact heat conduction and compaction-driven fluid flow in the Chesapeake Bay impact structure based on downhole vitrinite reflectance data, ICDP-USGS Eyreville deep core holes and Cape Charles test holes, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 905-930, 2009 |
| Marchand E., Whitehead J., Statistical Evaluation of Compositional Differences Between Upper Eocene Impact Ejecta Layers, 2002. |
| Mayr, S.I., et al., Physical rock properties of the Eyreville core, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 137-163, 2009 |
| McDonald, I., Bartosova, K., Koeberl, C., Search for a meteoritic component in impact breccia from the Eyreville core, Chesapeake Bay impact structure: Considerations from platinum group element contents, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 469-479, 2009 |
| Mchugh, C. M. G., Paterson, T., Snyder, S.W., Miller,K.G., Dynamics of Chesapeake Bay Impact reavealed by upper Eocene ejecta deposition on the New Jersey continental margin. GSA Salt Lake City '97, Annual-Meeting Abstracts. Abs. No. 50048. 1997. |
| McHugh, C. M. G., Snyder, S. W., Miller., Upper Eocene Ejecta of the New Jersey Continental Margin reveal Dynamics of Chesapeake Bay Impact, EPSL v. 160 pp. 353-367. 1998. |
| Monastersky, R., Large meteorite scar identified in Virginia. Science News, v. 146, pp. 116-117. 1994. |
| Obradovich, J. D., Snee, L. W. and G. A. Izett., Is there more than one glassy impact layer in the Late Eocene? Geological Society of America Abstracts with Program, v 21, p 134. 1989. |
| Ormo, J., et al., Comparison of clast frequency and size in the resurge deposits at the Chesapeake Bay impact structure (Eyreville A and Langley cores): Clues to the resurge process, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 617-632, 2009 |
| Ormo, J., et al., Water resurge at marine-target impact craters analyzed with a combination of low-velocity impact experiments and numerical simulations, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 465, pp. 81-101, 2010 |
| Ormo, J., Lindstrom, M., When a cosmic impact strikes the sea bed, Geol. Mag. V.137(1), p.67-80. 2000. |
| Ormo, J., Next step in marine impact studies: combining geological data with numerical simulations for applications in planetary research, Workshop on Impact Cratering. 2003. |
| Pierce, H.A., Audio-magnetotelluric (AMT) soundings across the margin of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, York-James and Middle Peninsulas, Virginia, US Geological Survey Professional Paper, Issue 1688, pp. J1-J17, 2006 |
| Pierce, H.A., Murray, J.B., Physical property data from the ICDP-USGS Eyreville cores A and B, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Virginia, USA, acquired using a multisensor core logger, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 165-179, 2009 |
| Plado J., Pesonen L.J., Puura V., Gravity and Magnetic Modeling of a Complex Impact Structure - Effect of Deformation and Erosion, 1997. |
| Plescia, J.B., Daniels, D.L., Shah, A.K., Gravity investigations of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 181-193, 2009 |
| Poag, C. W., Aubry, M. -P., Upper Eocene impactites of the U.S. East coast: Depositional origins, biostratigraphic framework, and correlation. Palaios, v. 10, pp. 16-43. 1995. |
| Poag, C. W., Depositional regimes during emplacement of the exmore breccia (Chesapeake Bay Impact Crater): Clues from downhole geophysical logs, 1999 GSA Annual Meeting - Denver, Colorado. Abs. No. 50647. 1999. |
| Poag, C. W., Geophysical signature of the Chesapeake Bay impact crater (Late Eocene) (abstract). Meteoritics, v. 30, pp. 561-562. 1995. |
| Poag, C. W., Geophysical signature of the Chesapeake Bay impact crater (Late Eocene) (abstract). Meteoritics, v. 30, pp. 561-562. 1995. |
| Poag, C. W., Hutchinson, D. R., Colman., The Exmore Breccia: Impact Deposit of the Chesapeake Bay Crater, GSA Abstracts with Programs, 1996, Session 72. P. 181, Abstr. 54. 1996. |
| Poag, C. W., Hutchinson, D.R. and Colman,S.M., The Chesapeake Bay impact crater: An update (abstract). Lunar and Planetary Science XXVIII, p. 1119. 1997. |
| Poag, C. W., Late Eocene star wars: The Toms Canyon and Chesapeake Bay impact craters, U.S. east coast (abstract). Meteoritics, v. 30, pp. 562. 1995. |
| Poag, C. W., Powars, D.S., Poppe, L.J. and Mixon,R.B., Meteorid mayhem in Ole Virginny: Source of the North American tektite strewn field. Geology, v. 22, pp. 691-694. 1994. |
| Poag, C. W., Powars, D.S., Poppe, L.J., Mixon, R.B., Edwards, L.E., Folger, D.W. and Bruce,S., Deep sea drilling project Site 612 bolide event: New evidence of a late Eocene impact-wave deposit and a possible impact site, U.S. east coast. Geology, v. 20, pp. 771-774. 1992. |
| Poag, C. W., Secondary Craters from the Cesapeake Bay Impact, LPSC XXX, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, TX, Abstr. 1047 (CD-ROM). 1999. |
| Poag, C. W., Structural outer rim of Chesapeake Bay impact crater: Seismic and bore hole evidence. Meteoritics & Planetary Science, v. 31, pp. 218-226. 1996. |
| Poag, C. W., The Chesapeake Bay bolide impact: a convulsive event in Atlantic Coastal Plain evolution. Sedimentary Geology, v. 108, pp. 45-90. 1997. |
| Poag, C. W., The Chesapeake Bay Bolide Impact: A new view of coastal plain evolution, USGS - U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet FS-049-98. ONLINE http://marine.er.usgs.gov/fact-sheets/fs49-98/. 1998. |
| Poag, C. W., The Chesapeake Bay structure: Earth's largest submarine peak-ring impact crater (abstract). Large Meteorite Impacts and Planetary Evolution,. 1997. |
| Poag, C.W., Coring the Chesapeake Bay impact crater, Geotimes, v. 49, pp. 22-25, 2004 |
| Poag, C.W., Eastern rim of the Chesapeake Bay impact crater: Morphology, stratigraphy, and structure, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 384, pp. 117-130, 2005 |
| Poag, C.W., Paleoenvironmental recovery from the Chesapeake Bay bolide impact: The benthic foraminiferal record, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 747-773, 2009 |
| Poag, C.W., Plescia, J.B., Molzer, P.C., Ancient impact structures on modern continental shelves: The Chesapeake Bay, Montagnais, and Toms Canyon craters, Atlantic margin of North America, Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, v. 49, pp. 1081-1102, 2002 |
| Poag, C.W., Synimpact-postimpact transition inside Chesapeake Bay crater, Geology, v. 30, pp. 995-998, 2002 |
| Pope, K., Ocampo, A.C., Kinsland, G.L., Smith,R., Surface Expression of the Chicxulub Crater, Geology; June 1996, v. 24; no. 6; p. 527-30. 1996. |
| Powars D.S., Johnson G.H., Edward L.E., Horton J.W. and others, An Explanded Chesapeake Bay Impact Structure, Eastern Virginia - New Corehole and Geophysical Data, 2002. |
| Powards, D. S., Quick, J.E., Scott, B.T., Catchings, R.D., Emry, S.R., Gohn, G.S., Izett, G.A., Johnson, G.H., Levine, J.S., McFarland, R.E., Poag,C.W., Structure and composition of the southwestern margin of the buried Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Bolide Impacts on Wet Targets, Geological Society of America Field Forum Abstracts. 2001. |
| Powars, D. S., Bruce, T. S., The Effects of the Chesapeake Bay Impact Crater on the Geological Framework and Correlation of Hydrogeologic Units of the Lower York-James Peninsula, Virginia, USGS Proffesional Paper 1612. |
| Powars, D. S., Johnson, G.H., Bruce, T.S., Edwards,L.E., The relation between the Chesapeake Bay Impact Structure and the structure and stratigraphy of Cenozoic deposits in eastern Virginia, GSA 2001 Southeastern Section - 50th Annual Meeting (April 5-6, 2001) Raleigh, North Carolina http://gsa.confex.com/gsa/2001SE/finalprogram/abstract_4706.htm. 2001. |
| Powars, D. S., The effects of the Chesapeake Bay Impact Crater on the Geologic Framework and the Correlation of Hydrogeologic Units of Southeastern Virginia, South of the James River, USGS Professional Paper 1622. 1999. |
| Powars, D.S., et al., High-resolution seismic-reflection images across the ICDP-USGS Eyreville deep drilling site, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 209-233, 2009 |
| Powars, D.S., et al., Physical stratigraphy of the upper Eocene to quaternary postimpact section in the USGS-NASA Langley core, Hampton, Virginia, US Geological Survey Professional Paper, Issue 1688, pp. G1-G37, 2006 |
| Powledge, F., Chesapeake Bay Restoration: A Model of What? BioScience, Vol. 55, No. 12, P. 1032 - 1038. 2005. |
| Pusz, A.E., et al., Stable isotopic response to late Eocene extraterrestrial impacts, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 452, pp. 83-95, 2009 |
| Reimold, W.U., et al., Petrographic observations on the Exmore breccia, ICDP-USGS drilling at Eyreville, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, USA, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 655-698, 2009 |
| Rostad, C.E., Sanford, W.E., Polar organic compounds in pore waters of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Eyreville core hole: Character of the dissolved organic carbon and comparison with drilling fluids, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 891-903, 2009 |
| Sanford, W.E., A simulation of the hydrothermal response to the Chesapeake Bay bolide impact, Geofluids, v. 5, pp. 185-201, 2005 |
| Sanford, W.E., et al., Drilling the central crater of the chesapeake bay impact structure: A first look, Eos, v. 85, pp. 369+377, 2004 |
| Sanford, W.E., et al., Pore-water chemistry from the ICDP-USGS core hole in the Chesapeake Bay impact structure-Implications for paleohydrology, microbial habitat, and water resources, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 867-890, 2009 |
| Schmitt, R.T., et al. , Geochemistry of impactites and crystalline basement-derived lithologies from the ICDP-USGS Eyreville A and B drill cores, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Virginia, USA, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 481-541, 2009 |
| Schulte, P., et al., The Eocene-Oligocene sedimentary record in the Chesapeake Bay impact structure: Implications for climate and sea-level changes on the western Atlantic margin, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 839-865, 2009 |
| Self-Trail, J.M., Edwards, L.E., Litwin, R.J., Paleontological interpretations of crater processes and infilling of synimpact sediments from the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 633-654, 2009 |
| Self-Trail, J.M., Shock-wave-induced fracturing of calcareous nannofossils from the Chesapeake Bay impact crater, Geology, v. 31, pp. 697-700, 2003 |
| Shah, A.K., et al., Megablocks and melt pockets in the Chesapeake Bay impact structure constrained by magnetic field measurements and properties of the Eyreville and Cape Charles cores, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 195-208, 2009 |
| Shah, A.K., et al., New surveys of the Chesapeake Bay impact structure suggest melt pockets and target-structure effect, Geology , v. 33, pp. 417-420, 2005 |
| Skála, R., Langenhorst, F., Deutsch, A. , Geochemical characteristics of basement target rocks, suevitic glasses from the Eyreville B drill core, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, and three bediasites, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 435-445, 2009 |
| Thomas, W. A., Chowns, T.M., Daniels, D.L., Neathery, T.L., Glover III, L. and Gleason,R.J., The subsurface Appalachians beneath the Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plains. Eds., Hatcher, R.D. Jr., Thomas, W.A. and Viele, G.W. in "The Appalachian-Ouachita Orogen in the United States", Boulder, Colorado, Geological Society of America, The Geology of North America, V. F-2, pp. 445-458. 1989. |
| Townsend, G.N., et al., Petrographic and geochemical comparisons between the lower crystalline basement-derived section and the granite megablock and amphibolite megablock of the Eyreville B core, Chesapeake Bay impact structure, USA, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 255-275, 2009 |
| Tsikalas, F., Faleide, J.I., Post-impact structural crater modification due to sediment loading: An overlooked process, Meteoritics and Planetary Science, v. 42, pp. 2013-2029, 2007 |
| Tsikalas, F., Post-Impact modification correction factor: a necessity to better constrain cratering scaling law estimates and impact-related consequences at all buried impact craters, Lunar and Planetary Science XXXIX, abstract #1009. 2008. |
| Turtle, E.P., et al., Impact structures: What does crater diameter mean?, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 384, pp. 1-24, 2005 |
| Vanko, D.A., A petrographic and fluid inclusion assessment of hydrothermal alteration of some impactites and crystalline rocks in the Chesapeake Bay impact structure, ICDP-USGS Eyreville B core, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 543-557, 2009 |
| Whitehead, J., Grieve, R. A. F., Shocked basement rocks from within the proposed Chesapeake Bay impact drill core, USGS Open File Report 1016. ICDP-USGS Workshop on the drilling in the central crater of the Chesapeak Bay impact structure, Virginia, USA: Proceedings Volume. p. 83-84. 2004. |
| Wilhelm, H., Burkhardt, H., Popov, Y., Heidinger, P., Mayr, S. I., Romushkevich, R., & Gorobtsov, D., The thermo-hydraulic regime of the chesapeake bay impact structure. Paper presented at the , 43(5) 437-437. 2011. |
| Wittman, A., et al., Petrology of impact melt rocks from the Chesapeake Bay crater, USA, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 377-396, 2009 |
| Wittman, A., et al., The record of ground zero in the Chesapeake Bay impact crater-Suevites and related rocks, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 349-376, 2009 |
| Wright Horton Jr., J., et al., Geologic columns for the ICDP-USGS Eyreville B core, Chesapeake Bay impact structure: Impactites and crystalline rocks, 1766 to 1096 m depth, Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, Issue 458, pp. 21-49, 2009 |
| * pre-1977 K-Ar, Ar-Ar and Rb-Sr ages recalculated using the decay constants of Steiger and Jager (1977) Ages in millions of years (Ma) before present. ** Abbreviations: C - Crystalline Target; C-Ms - Metasedimentary Target; M - Mixed Target (i.e.sedimentary strata overlying crystalline basement); S - sedimentary target (i.e. no crystalline rocks affected by the impact event). From Osinski. G. R., Spray J. G., and Grieve R. A. F. 2007. Impact melting in sedimentary target rocks: A synthesis. In The Sedimentary Record of Meteorite Impacts, Geological Society of America Special Paper. Editors: Evans K. Horton W., King D., Morrow J., and Warme J. Geological Society of America: Boulder, in press. ***From Koeberl,C. Identification of meteoritic components in impactites. 1998, Koeberl, C. The Geochemistry and Cosmochemistry of Impacts. 2007 and PASSC Files. (IAB, IIIAB, IIIB, IIID - Iron Meteorite) |