Acraman
| Crater Name | Location | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter (km) | Age (Ma) | Exposed | Drilled | Target Rock** | Bolide Type*** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acraman | South Australia | S 32° 1' | E 135° 27' | 90 | ~ 590 | Y | N | C | Chondrite |
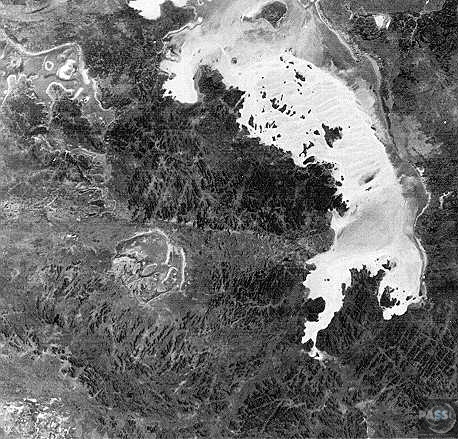
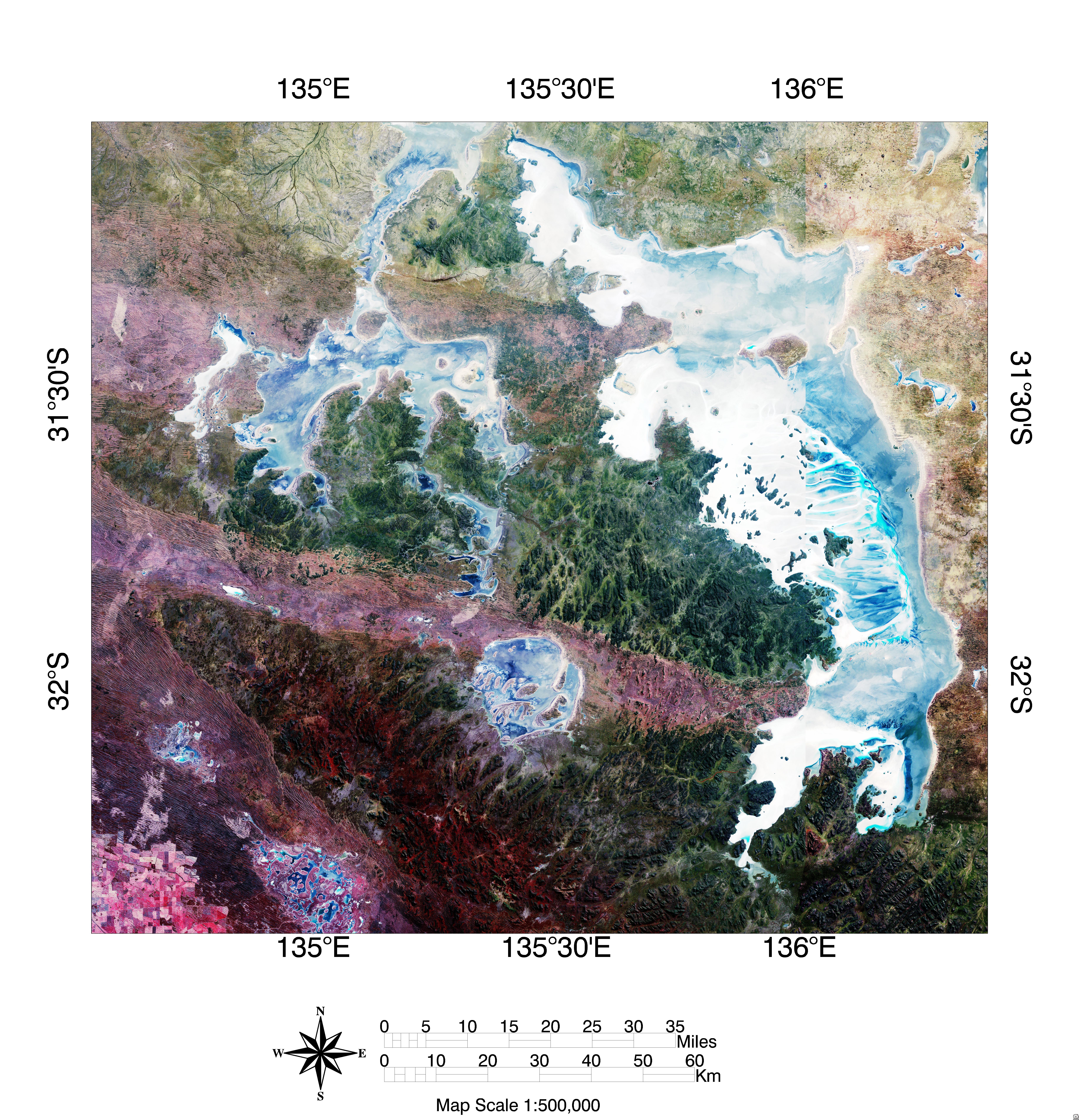
1. Landsat image
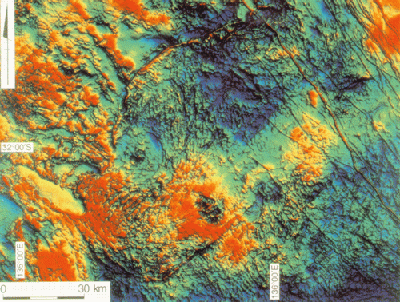
2. Aeromagnetic image of the Acraman area of the Gawler Craton, covering the Landsat scene (see image below). ER Mapper file: total magnetic intensity, pseudocolor (Gaussian equalisation histogram stretch), sun angle from the northeast. From Williams, Schmidt and Boyd (1996).
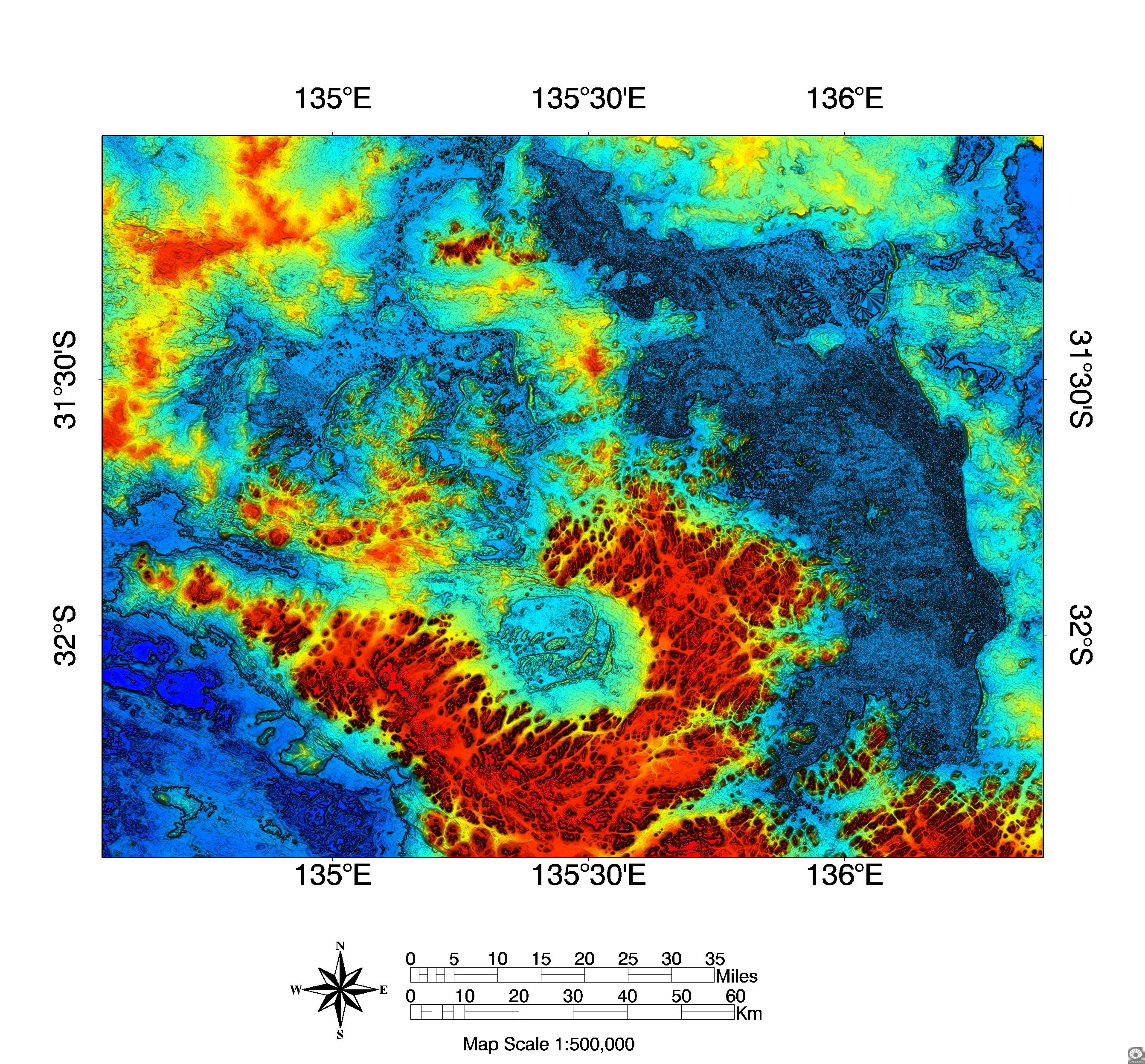
3. Landsat scene covering most of the Acraman impact structure in the Mesoproterozoic Gawler Range Volcanics, showing: 1, Lake Acraman within the Acraman depression; 2, Lake Gairdner; 3, Lake Everard; 4, the Yardea corridor at 85-90 km diameter. Surface water (darker blue) in Lake Gairdner helps define an arcuate trend (5) at ~150 km diameter that continues westward to Lake Everard. X marks the location of a central dipolar magnetic anomaly in the southeastern part of Lake Acraman. Landsat scene 15 February 1973, scene center S31-30 E135-51. From Williams, Schmidt and Boyd (1996).
4. DEM Image Provided by Dr. Carlos Roberto de Souza Filho
5 & 6. Image Provided by Dr. Carlos Roberto de Souza Filho
References |
Arouri, K., et al., Reconnaissance sedimentology and hydrocarbon biomarkers of Ediacarian microbial mats and acritarchs, lower Ungoolya Group, Officer Basin, Precambrian Research , v. 100, pp. 235-280, 2000 |
Baldwin, S. L., McDougall, I. and Williams,G.E., K/ Ar and 40Ar/39Ar analyses of meltrock from the Acraman impact structure, Gawler Ranges, South Australia. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, v. 38, pp. 291-298. 1991. |
Cockell, C. S., Lee, P., The Biology of Impact Craters - a review. Biol. Rev., 77, P. 279 - 310. 2002. |
Glikson, A. Y., Mega-impacts and mantle-melting episodes: tests of possible correlations. AGSO Journal of Australian Geology & Geophysics, v. 16, pp. 587-607. 1996. |
Gostin, V. A., Haines. P.W., Jenkins, R.J.F., Compston, W. and Williams,I.S., Impact ejecta horizon within late Precambrian shales, Adelaide geosyncline, South Australia. Science, v. 233, pp. 198-200. 1986. |
Gostin, V. A., Keays, R.R. and Wallace,M.W., Iridium anomaly from the Acraman impact ejecta horizon: Impacts can produce sedimentary iridium peaks. Nature, v. 340, pp. 542-544. 1989. |
Gostin, V. A., Keays, R.R. and Wallace,M.W., The Acraman impact and its widespread ejecta, South Australia (abstract). International Conference on Large Meteorite Impacts and Planetary Evolution, LPI Contrib. No. 746, pp. 30-31. 1992. |
Gostin, V. A., Wallace, M.W. and Keays,R.R., Sedimentology and geochemistry of the Bunyeroo impact ejecta horizon, South Australia (abstract). International Workshop on Meteorite Impact on the Early Earth, Perth, Australia, Contrib. No. 746, pp. 16-17. 1990. |
Gostin, V.A., Zbik, M., Petrology and microstructure of distal impact ejecta from the Flinders Ranges, Australia, Meteoritics and Planetary Science, v. 34, pp. 587-592, 1999 |
Grey, K., Walter, M.R., Calver, C.R., Neoproterozoic biotic diversification: Snowball Earth or aftermath of the Acraman impact?, Geology, v. 31, pp. 459-462, 2003 |
Grieve, R. A. F., Meteorite impact studies featured in Australia. Episodes, v. 13, pp. 281-282. 1990. |
Grieve, R. A. F., The record of impact on Earth: Implications for a major Cretaceous/Tertiary impact event. Geological Society of America, Special Paper 190, pp. 25-37. 1982. |
Gurov, E. P., Gurova, E. P., Impact structures on the Earth's surface (in Russian). Geologicheskii Zhurnal, v. 47, pp. 117-124. 1987. |
Gurov, E. P., The Acraman impact structure: Estimation of the diameter by the ejecta layer thickness (abstract). Lunar and Planetary Science XXIV, pp. 589-590. 1993. |
Haines P. W., Tekite-bearing flood deposites in NE Thailand - Palaemagnetic evidence suggests deposition comtemporaneous with - 0.8 MA impact, 2004. |
Haines, P. W., Impact Cratering and Distal Ejecta: The Australian Record. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 52, P. 481 - 507. 2005. |
Hawke, P. J., A re-evaluation of the size of the Acraman Impact Structure, Australia, 2003. |
Hill, A. C., Gorjan, P. , Walter, M. R., Carbon, Nitrogen and Sulfur stable-isotope changes before and after the ~580 MA (Late Neoproterozoic) Acraman Impact Event. 17th Australian Geological Convention, P. 233. 2004. |
Hill, A.C, et al., New records of Ediacaran Acraman ejecta in drillholes from the Stuart Shelf and Officer Basin, South Australia, Meteoritics and Planetary Science, v. 42, pp. 1883-1892, 2007 |
Hill, A.C, et al., New records of Late Neoproterozoic Acraman ejecta in the Officer Basin, Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, v. 51, pp. 47-51, 2004 |
Keays, R., Schaefer, B., Wallace, M., Lambert,D., The Acraman Impact Event Horizon: Relative contributions of meteoritic, diagenetic and host rock Cu and PGE from Re-Os Isotopes, 17th Australian Geological Convention, Hobart, Tasmania 8-13th Feb 2004. 2004. |
Koeberl, C., Martinez-Ruiz, F., The Stratigraphic Record of Impact Events: A Short Overview, Impact Markers in the Stratigraphic Record p. 1 - 40. 2003. |
Masaitis, V. L., Danilin, A.N., Maschak, M.S., Raykhlin, A.I., Selivanovskaya, T.V. and Shadenkov,Ye.M., The Geology of Astroblemes (in Russian). Leningrad, Nedra, 231 p. 1980. |
McKirdy, D. M., Webster, L. J. , Arouri, K. R. , Grey, K. and Gostin, V. A., Contrasting sterane signatures in Neoproterozoic marine rocks of Australia before and after the Acraman asteroid impact. Organic Geochemistry 37 P. 189 - 207. 2006. |
Miura, Y., Kato, T., Anomalous shocked quartz in Australian impact craters (abstract). Meteoritics, v. 26, pp. 373. 1991. |
Pufahl P., James N., Bone Y., Lukasik J., Plocene sedimentation in a shallow, coolwater, marine culf, Murray Basin, South Australia, 2004. |
Raub, T. D., Evans, D. A. D., Global Setting of the Acraman Impact: Magnetostratigraphy as a relative chronometer with Palaeogeographic power, 17th Australian Geological Convention, Hobart, Tasmania 8-13th Feb 2004. 2004. |
Schmidt, P. W., Williams, G. E., Palaeomagnetic correlation of the Acraman impact structure and the Late Proterozoic Bunyeroo ejecta horizon, South Australia. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, v. 38, pp. 283-289. 1991. |
Schmidt, P. W., Williams, G. E., Palaeomagnetism of the ejecta-bearing Bunyeroo Formation, late Neoproterozic, Adelaide fold belt, and the age of the Acraman impact. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, v. 144, pp. 347-357. 1996. |
Shoemaker, E. M., Shoemaker, C. S., Impact structures of Australia (1987) (abstract). Lunar and Planetary Science XIX, pp. 1079-1080. 1988. |
Shoemaker, E. M., Shoemaker, C. S., Proterozoic impact record of Australia (abstract). Abstracts of the International Workshop on Meteorite Impact on the Early Earth, Perth, Australia, pp. 47-48. 1990. |
Shoemaker, E. M., Shoemaker, C. S., The Proterozoic impact record of Australia. AGSO Journal of Australian Geology & Geophysics, v. 16, pp. 379-398. 1996. |
Sutherland, F. L., Meteoritic versus volcanic events at the Cretaceous Tertiary boundary - An Australian perspective. 1990. |
Wallace, M. W., Gostin, V.A. and Keays,R.R., Acraman impact ejecta and host shales: Evidence for low-temperature mobilization of iridium and other platinoids. Geology, v. 18, pp. 132-135. 1990. |
Wallace, M. W., Gostin, V.A. and Keays,R.R., Discovery of the Acraman impact ejecta blanket in the Officer Basin and its stratigraphic significance. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, v. 36, pp. 585-587. 1989. |
Wallace, M. W., Gostin, V.A. and Keays,R.R., Sedimentology of the Neoproterozoic Acraman impact- ejecta horizon, South Australia. AGSO Journal of Australian Geology & Geophysics, v. 16, pp. 443-451. 1996. |
Wallace, M. W., Gostin, V.A. and Keays,R.R., Spherules and shard-like clasts from the late Proterozoic Acraman impact ejecta horizon, South Australia. Meteoritics, v. 25, pp. 161-165. 1990. |
Wallace, M. W., Gostin, V.A. and Keays,R.R., Spherules and shard-like clasts from the late Proterozoic Acraman impact ejecta horizon, South Australia. Meteoritics, v. 25, pp. 161-165. 1990. |
Wallace, M. W., Keays, R.R. and Gostin,V.A., Sedimentology of the Late Proterozoic Acraman impact ejecta horizon, South Australia (abstract). GAC/MAC, p. A100. 1996. |
Wallace, M. W., Williams, G.E., Gostin, V.A. and Keays,R.R., The late Proterozoic Acraman impact - Towards an understanding of impact events in the sedimentray record. Mines and Energy Review, South Australia, No. 157, pp. 29-35. 1990. |
Whitehead J., Ehrmann W., Hillenbrand C-D., Hart C., Harwood D. and Tavian M., Micene marine strata from inland Antarctica - Palaeoenvironmental reconstruction from diatom, mollusc, sediment and geochemical evidence, 2004. |
Williams, G. E., Acraman, South Australia: Australia's largest meteorite impact structure. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Victoria, v. 106, pp. 105-127. 1994. |
Williams, G. E., Acraman: A major impact structure from the Neoproterozoic of Australia. Geological Society of America Special Paper 293, pp. 209-224. 1994. |
Williams, G. E., Boyd, D. and Schmidt,P., Aeromagnetic images of the Acraman impact structure. The Australian Geologist, v. 97,. 1995. |
Williams, G. E., Gostin, V. A., Acraman - Bunyeroo impact event ( Ediacaran), South Australia, and environmental consequences: twenty five years on, Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 52, P. 607 - 620. 2005. |
Williams, G. E., Schmidt, P.W. and Boyd,D.M., Magnetic signature and morphology of the Acraman impact structure, South Australia. AGSO Journal of Australian Geology & Geophysics, v. 16, pp. 431-442. 1996. |
Williams, G. E., The Acraman impact structure, South Australia (abstract). International Workshop on Meteorite Impact on the Early Earth, Perth, Australia, LPI Contrib. No. 746, pp. 60-61. 1990. |
Williams, G. E., The Acraman impact structures: Source of ejecta in late Precambrian shales, South Australia. Science, v. 233, pp. 200-203. 1986. |
Williams, G. E., The Acraman structure - Australia's largest impact scar. Search, v. 18, pp. 143-145. 1987. |
Williams, G. E., Wallace, M. W., The Acraman asteroid impact, South Australia: magnitude and implications for the late Vendian environment. Journal of the Geological Society of London, vol. 160, p. 545-554. 2003. |
Williams, G., Gostin, V., Wallace., The Acraman Impact Event, South Australia: Recognition, Manitude and Implications for the Late Vendian Environment, 17th Australian Geological Convention, Hobart, Tasmania 8-13th Feb 2004. 2004. |
Williams, G.E., Gostin, V.A., Geomorphology of the Acraman impact structure, Gawler Ranges, South Australia, Cadernos do Laboratorio Xeoloxico de Laxe, Issue 35, pp. 209-219, 2010 |
| * pre-1977 K-Ar, Ar-Ar and Rb-Sr ages recalculated using the decay constants of Steiger and Jager (1977) Ages in millions of years (Ma) before present. ** Abbreviations: C - Crystalline Target; C-Ms - Metasedimentary Target; M - Mixed Target (i.e.sedimentary strata overlying crystalline basement); S - sedimentary target (i.e. no crystalline rocks affected by the impact event). From Osinski. G. R., Spray J. G., and Grieve R. A. F. 2007. Impact melting in sedimentary target rocks: A synthesis. In The Sedimentary Record of Meteorite Impacts, Geological Society of America Special Paper. Editors: Evans K. Horton W., King D., Morrow J., and Warme J. Geological Society of America: Boulder, in press. ***From Koeberl,C. Identification of meteoritic components in impactites. 1998, Koeberl, C. The Geochemistry and Cosmochemistry of Impacts. 2007 and PASSC Files. (IAB, IIIAB, IIIB, IIID - Iron Meteorite) |



.jpg)